By default, the FiveNines agent expects Docker to be running as root. If you are using Rootless Docker, the agent cannot see your containers because they run inside a private user namespace that is invisible to the rest of the system.
To enable monitoring, you must expose the Rootless Docker API to the host system using a TCP port.
The Challenge: Network Isolation
In Rootless mode, Docker runs inside a "User Namespace." Even if you enable TCP listening in the Docker config, the port opens inside that namespace, remaining invisible to the FiveNines agent.
To fix this, we must use RootlessKit to punch a hole through the namespace and expose the port to the OS.
Step 1: Configure the Service Override
Log in as the user running Docker (not root).
We will override the systemd startup command to bind Docker to port 2375 and map that port to the host.
-
Edit the user-level docker service:
systemctl --user edit docker -
Copy and paste the following block into the editor.
(Note: Replace
1000in the socket path with your user's UID if it is different. Runid -uto check).[Service] # 1. Clear the default startup command ExecStart= # 2. Start Docker listening on both Socket and TCP (inside the namespace) ExecStart=/usr/bin/dockerd-rootless.sh -H unix:///run/user/1000/docker.sock -H tcp://0.0.0.0:2375 # 3. Expose the inner port 2375 to the host's port 2375 Environment=DOCKERD_ROOTLESS_ROOTLESSKIT_FLAGS="-p 0.0.0.0:2375:2375/tcp" -
Save and exit.
Step 3: Apply Changes
Reload the service manager and restart Docker to apply the networking changes.
systemctl --user daemon-reload
systemctl --user restart docker
Verification:
Run this command to ensure the port is now open on the host:
ss -tulpn | grep 2375
You should see a line indicating a process is listening on port 2375.
Step 4: Configure the FiveNines Agent
Now that the port is accessible, tell the FiveNines agent to connect via TCP instead of looking for a socket file with the following URL:
tcp://127.0.0.1:2375
Go to the instance settings on the FiveNines platform and enable Docker monitoring:
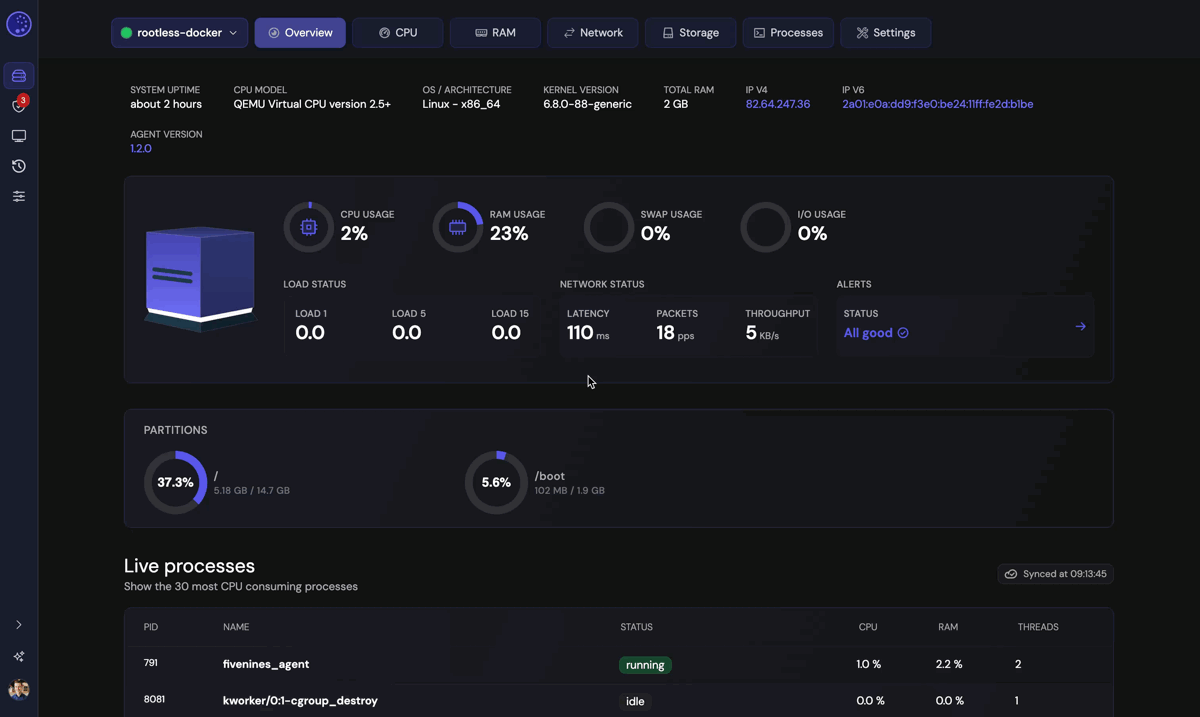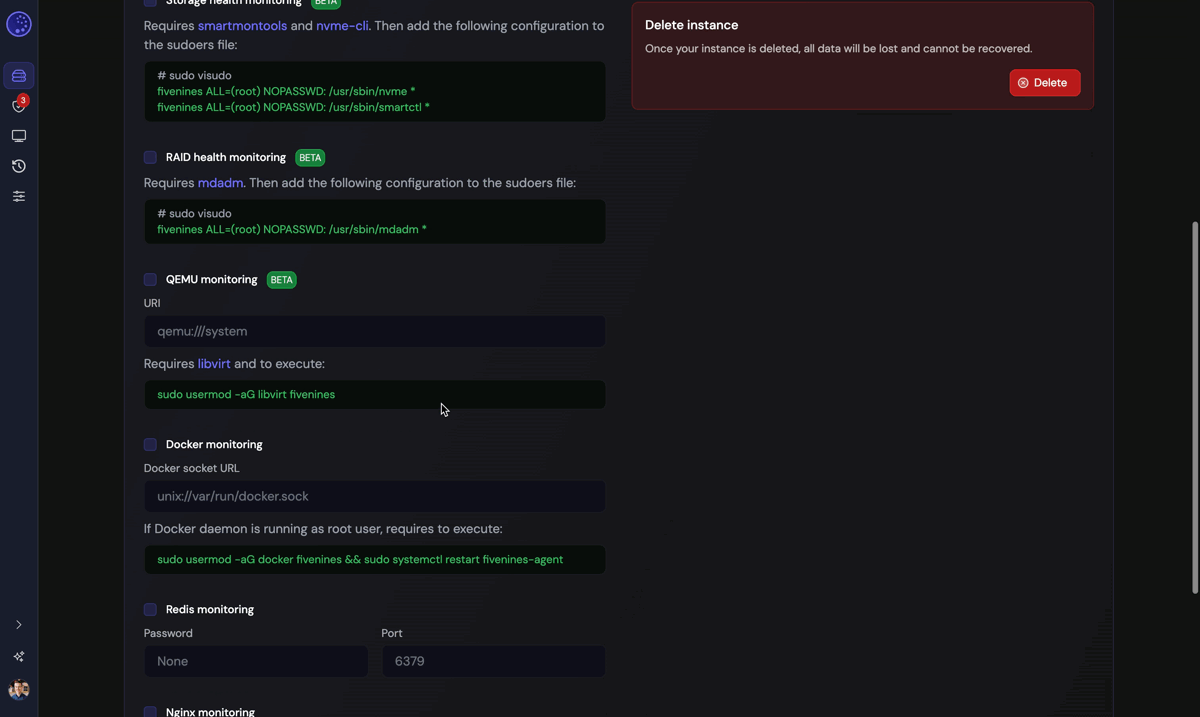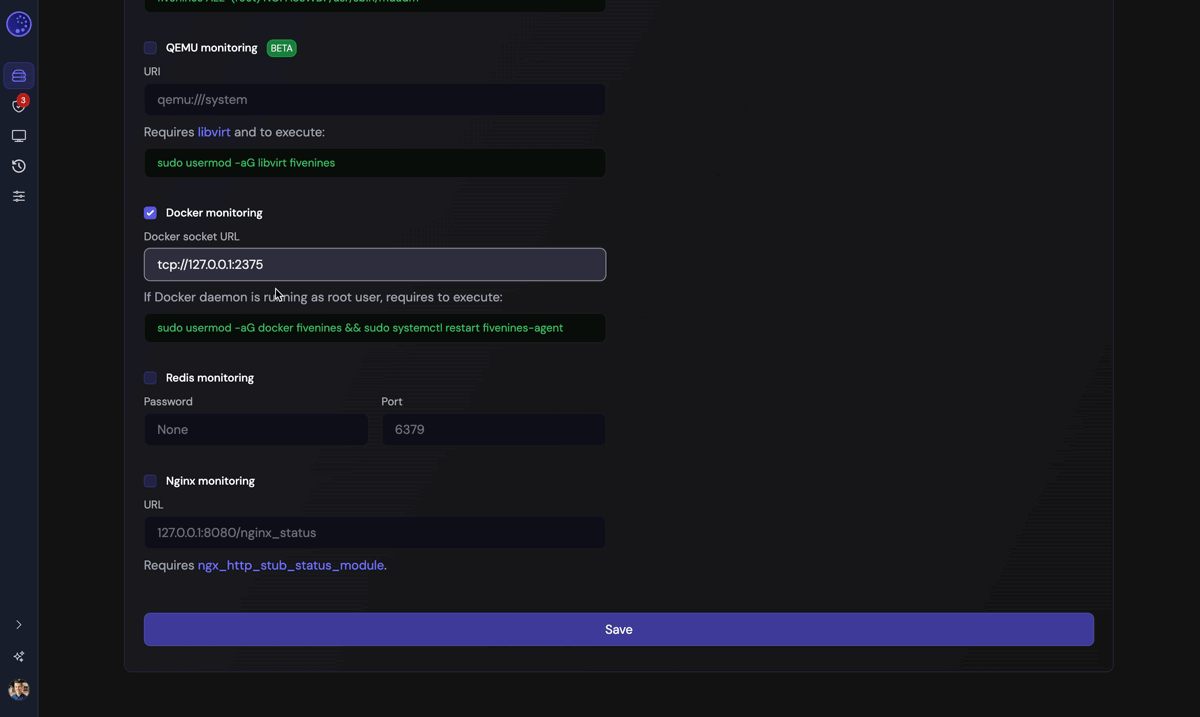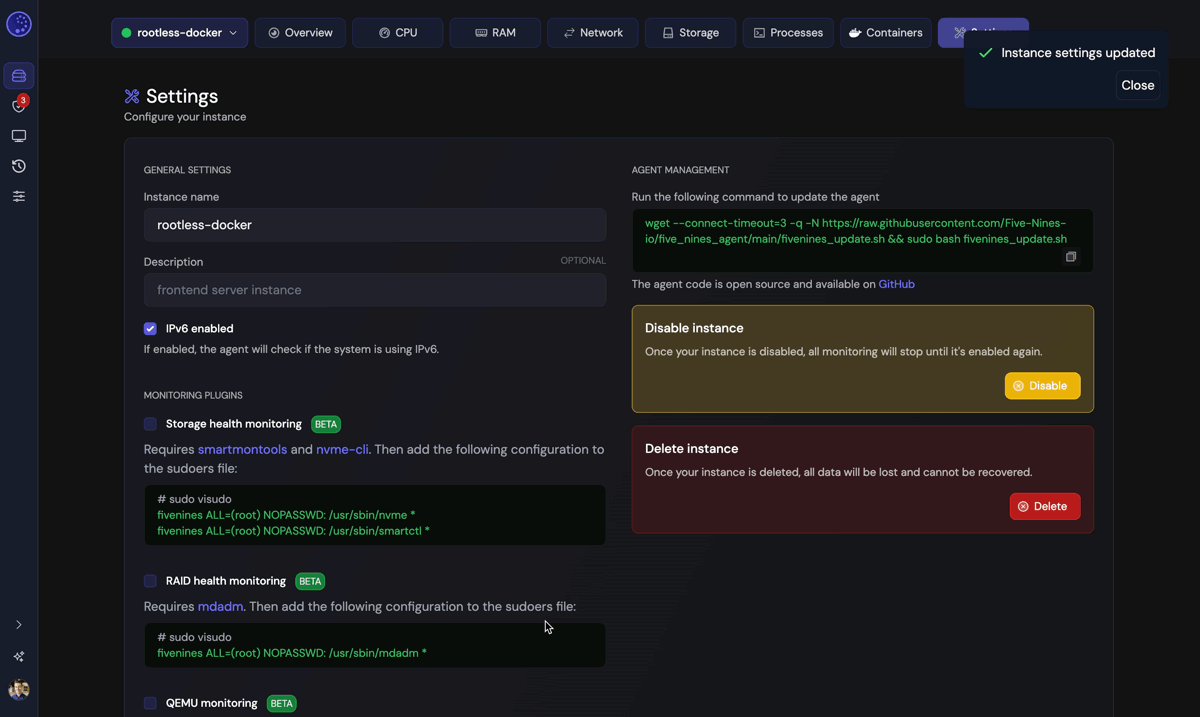
Wait a couple of minutes and should see data coming through the interface.
Troubleshooting
Connection Refused
If the agent still cannot connect:
-
Run
systemctl --user status dockerand ensure the service is Active (running). -
If the service failed, check for conflicts in
~/.config/docker/daemon.json
Permission Denied or Socket Missing
Ensure you used the correct UID in Step 2. The path /run/user/1000/docker.sock is standard for the first user on a system, but other users may have 1001, 1002, etc.